

Home | Testing Services | Technical Information | Consulting | Customer Services | Careers | Contact Us
►TOYS
In-depth Explanation on EN 71-1:2005 + A6:2008 Safety of Toys, Mechanical and Physical Properties
REQUIREMENTS
FOR BOTH THE AGE GROUPS: 0 – 3 YEARS & 3 YEARS AND
UP (i.e. ALL AGES)
1. ASSEMBLED TOYS

If a toy is intended to be assembled by adult, any applicable requirements
in EN 71-1 apply to the toys in assembled stage only (and not to that in the
un-assembled stage), provided that there are:
-
detailed assembly instructions
-
an statement in pa
“This toy is intended to be assembled by adult”
2.
FLEXIBLE PLASTIC SHEETING
Sheets (e.g. apron) without ba
3.
TOY BAGS

Toy bags with an opening
perimeter greater than 380 mm having a drawstring shall either:
-
Be made of material permeable
to air; or
- have a total
ventilation area of 1300 mm2 minimum through at least 2 holes at
least 150 mm apart or through and equivalent single ventilation area
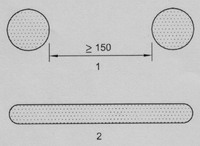
Dimensions in millimeters
Key
1.
Total ventilation area, 1300 mm2
or more
2.
Alternative equivalent ventilation area, 1300
mm2 or more
Examples of ventilation
areas for toy bags
4. GLASS (age group of 3
years and up)

Accessible glass shall
only be used in either of the following conditions:
- Necessary to function
- Textile glass for reinforcement
- Solid glass marbles
- Solid glass eyes for dolls
5. EDGES
- The toys shall not have hazardous sharp edge (for metal and
glass only)
- The toys shall be free from hazardous burr (for metal and
plastic)
- For toys intended for children of 3 years and up, if functional
sharp edges exist (e.g. blade of pencil sharpener), warning is needed (see
below for an example)
“This
toy contains functional sharp edges”
6. POINTS 
- The toys shall not have hazardous sharp edge (for all material)
- For toys intended for children of 3 years and up, if functional
sharp points exist (e.g. needle of sewing machine), warning is needed (see
below for an example)
“This
toy contains functional sharp points”
7. PROTRUDING PARTS
- Hazardous projection shall be protected
- The protection shall be capable of withstanding a tension of 60 N
(13.5 lb)
8. DRIVING MECHANISMS

- Hazardous driving mechanism (e.g. gear box) shall not become
accessible or produces sharp point/edge after drop and impact tests
9. WINDING KEYS
-
Clearance between winding key
and toy body shall either be less than 5 mm or greater than 12 mm
-
Any holes in keys or handles
shall not premit the insertion of a 5 mm diameter rod
10. FOLDING AND SLIDING MECHANISMS

|
|
Toy
pushchair/perambulator WITH handle which can fold down over a child |
Toy
pushchair/perambulator WITHOUT handle which can fold down over a child |
|
No. of lo |
At least 2 lo Remark: 2 devices
of the same construction (e.g. lo |
At least 1 lo Remark: 2 devices
of the same construction (e.g. lo |
|
AUTOMATIC lo |
Yes, at least 1
automatic lo |
No, the lo |
|
Fully erected |
After the test
below, the toy shall not collapse and neither of the lo |
After the test
below, the toy shall not collapse and the lo |
|
Partially erected |
Partially erected
= the toy can erect without one or more of the lo After test
(below) in a partially erected orientation , the toy shall not collapse and
neither of the lo |
Partially erected
= the toy can erect without a lo After test
(below) in a partially erected orientation , the toy shall not collapse and
the lo |
|
Test Methods |
Loading mass : Toys labeled as
not suitable for children over 36 months: 25 kg Others: 50
kg
Procedures: 1.
Erecting
and folding the toy 10 times 2.
With
the lo 3.
If
the toy can be erected partially, also carry out the above loading test in
this orientation 4.
If
the seat of the body is detachable from the chassis, the above loading test
shall also be carried out on the chassis only using suitable support for the
loading mass |
Loading mass : Toys labeled as
not suitable for children over 36 months: 25 kg Others: 50
kg
Procedures: 1.
Erecting
and folding the toy 10 times 2.
With
the lo 3.
If
the toy can be erected partially, also carry out the above loading test in
this orientation |
11.
HINGES

-
If either one hinge arrangement
has a mass less than 250 g, hinge clearances shall not be evaluated
-
If both hinge arrangements have
masses more than 250 g, hinge clearances shall be evaluated, as follows:
Clearance < 5 mm : PASS
Clearance between 5 – 12 mm : FAIL
Clearance > 12 mm : PASS
12. MOUTH ACTUATED TOYS (e.g.
whistle)
- The toys shall not be small parts in as-received stages, even
they are intended for children 3 years and up
-
If the mouthpiece (e.g.
mouthpiece of a flute) is a small part, it shall not become loose before and
after soaking, torque and tension tests
-
If a toy contains loose object
(e.g. sphere in whistle) which is a small part, it shall not be released after
blowing and su
13. TOYS WHICH A CHILD CAN
ENTER
- The toys (if volume > 0.03 m3) shall provide 2
ventilation holes, each > 650 mm2 and situated at least 150mm
apart
-
It shall be possible to open
the door from inside using a force < 50 N (11.2 lb)
-
The total ventilation area
shall be provided when the toys are placed, in any position, adjacent to a
corner of a room
14. MASKS AND HELMETS
Masks and helmets that fully enclose the head and which are made of
impermeable material shall provide a total ventilation area of 1300 mm2
minimum through at least 2 holes at least 150 mm apart or through any
equivalent single ventilation area
15. RIGID TOYS THAT COVER
THE FACE (e.g. goggles, face shields)
There shall not be sharp point, sharp edge, or loose part after
torque, tension, drop, impact and compression tests
16. TOYS INTENDED TO BEAR THE MASS OF A CHILD (e.g. chairs,
skateboards, ro

Please see below for an example for the
testing of a tricycle (where the hands or feet provide the
motive power)
|
TEST ITEM |
REQUIREMENTS |
TEST METHODS |
|
Static Strength |
AFTER TEST: No sharp point No sharp edge No hazardous
accessible driving mechanism No collapse
resulting in failure(s) according to EN 71-1 |
Loading mass : Toys labeled as
not suitable for children over 3 years: 25 kg Others: 50
kg
Procedures: Load the toy in
most onerous position with an appropriate mass on its standing or sitting
surface for 5 min Where the toy is
intended to bear the mass of more than one child at a time, test every
sitting or standing are simultaneously.
|
|
Dynamic Strength |
AFTER TEST: No sharp point No sharp edge No hazardous
accessible driving mechanism No collapse
resulting in failure(s) according to EN 71-1 |
Drive the toy (loaded with
appropriate mass) 3 times at a steady speed of 2 m/s
perpendicularly into a non-resilient step with a height of 50 mm. See Figure below for
specifications of the loading masses a.
Toys intended for use sitting down The load is
placed on the sitting surface. The clamps of the articulated arms are
attached to the steering wheel or handlebar. b.
Toys intended for use standing The load is
placed on a platform (250 mm high) such that the load's centre of gravity is
400 mm above the standing surface. The clamps of the articulated arms are
attached to the steering wheel or handlebar. c.
Roller skates and toys without steering wheel or
handles The load is placed on the sitting/standing surface. The articulated
arms are secured to the sides of the load. |
|
Stability |
The toy shall not
tip after test |
Load the toy in
most onerous position with an appropriate mass (as specified for Static
Loading Test) on its standing or sitting surface. Place the toy on
a 10o slope in the most onerous position with respect to
stability. Where the toy is
intended to bear the mass of more than one child at a time, test every
sitting or standing are simultaneously. |
|
Wheels directly
propelled by pedals |
No slots or holes
with a width greater then 5 mm |
---- |
|
Spaces between
the wheels and the body |
Space < 5
mm à PASS 5 mm ≦Space < 12 mm
à FAIL Space ≧ 12 mm à PASS |
---- |
|
Tricycle provided
with push handle |
The toy shall be
constructed in such a way as to prevent entrapment of the child’s feet in the
pedals etc. whilst being pushed (for example, free-wheeling mechanism or foot
rests) |
---- |
|
Labelling |
The toy, when
appropriate, shall be accompanied by instruction for use, assembly and
maintenance instructions. The toy shall be
accompanied by instructions drawing attention to the need to carry out che Instruction shall
also be given as to correct assembly of the toy, indicating those parts which
can present dangers if it is not correctly assembled. Specific information
regarding suitable ground surface shall be given. |
---- |
|
Warning statement for toys that due to their construction, strength,
design or other factors are not suitable for children over 36 months |
“Warning!
Not to be used by children over 36 months” + a brief indication of the specific reason calling for
this restriction (e.g. insufficient strength) Remark: the age warning shall be legible at the point
of sale of the product. |
---- |
17.
TOY SCOOTERS

-
Definition of a toy scooter: free-wheeling toy scooter which is
propelled by the muscular action of the user and may be foldable or not,
intended for children with a body mass of 50
kg or less
-
Toy scooters are further sub-divided into 2 categories:
i) those intended for children with a body mass
of 20 kg or less,
ii) those
intended for children with a body mass of 50
kg or less,
-
The handles on toy scooters should have an end with a diameter of 40
mm or more
-
The diameter of the front wheel(s) on toy scooters should be 120 mm or
greater
-
Braking system:
Toy
scooters intended for children with a body mass of 20 kg or less
No braking system is
required.
Toy
scooters intended for children with a body mass of 50 kg or less
There
should be at least one braking system operating on the rear wheel.
The
braking system should comply with the requirements of brake performance
specified in EN 71 Part 1.
-
Strength of toy scooter steering tubes:
Loading test in
downward direction to steering tubes
A total of 100 kg dead-weight(s) is/are loaded to
the handle(s)
Loading test in
upward direction to steering tubes
A total of 50 kg dead-weight(s) is/are loaded to
the handle(s)
After loading
tests,
i)
steering tubes should not collapse which results in failure to comply
with EN 71 Part 1;
ii)
steering tubes should not separate into 2 or more parts;
iii)
lo
Key
1.
Dead-weight
2. Podium
Test of steering tubes
-
Loading tests for static strength:
Toy
scooters intended for children with a body mass of 20 kg or less
Toy scooters should be loaded with a
dead-weight of 50 kg.
After test, the following should not exist:
i)
sharp point
ii)
sharp edge
iii)
accessible hazardous driving mechanism
iv)
collapse which results in failure to comply with EN 71 Part 1
Toy
scooters intended for children with a body mass of 50 kg or less
Toy scooters should be loaded with a
dead-weight of 100 kg. After test, the following should not exist:
i)
sharp point
ii)
sharp edge
iii)
accessible hazardous driving mechanism
iv)
collapse which results in failure to comply with EN 71 Part 1
Key
1. Dead-weight, 50 kg or 100kg, where appropriate
Static strength test for toy scooters
-
Dynamic strength test:
Toy scooters should be
tested for dynamic strength. After test, the following should not exist:
i)
sharp point
ii)
sharp edge
iii)
accessible hazardous driving mechanism
iv)
collapse which results in failure to comply with EN 71 Part 1
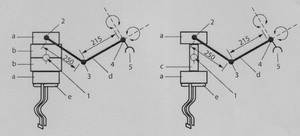
Dead-weight
for toys Dead-weight for
toys
intended
for children labeled as
not suitable for
of
over 36 months children of
over 36 months
Dimensions in millimeters
|
Specification of dead-weights for determination of
dynamic strength |
|||
|
Part |
Mass ( kg) |
Diameter (mm) |
Height (mm) |
|
A |
10.42 |
150 ± 2 |
75 ± 2 |
|
B |
14.58 |
178 ± 2 |
75 ± 2 |
|
C |
4.16 |
|
|
|
d (each) |
2.00 |
|
|
|
E |
0.50 |
|
|
Key
1.
Centre of gravity
2.
Spherical joint
3.
1-way joint
4.
2-way joint
5.
Clamp
6.
Articulated arms
7.
Cushion with
straps (removable)
18.
Heavy Immobile toys

-
Heavy Immobile toys are defined
as toys with masses > 4.5 kg
-
When placed on a 5o
inclined plane, the toys shall not tip over
19. PROJECTILE TOYS (e.g. toy guns, arrows…etc)
General requirements
-
All rigid projectiles shall
have tip radiuses of not less than 2 mm
-
Resilient materials used as
impact surfaces shall not become detached when subjected to a force of 60 N
(13.5 lb)
-
Projectiles with a suction cup
as impact area shall have a length of 57 mm or more, with its suction cup on a
flat surface under a force that is produced by its own weight

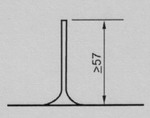
Measurement of length of bullets with suction cups
Dimensions
in millimeters
Projectile toys without stored energy
(i.e. controlled by the child)
- Darts shall have blunted points or points that are protected by
resilient material (e.g. rubber) whose area shall be > 3 cm2
- Helicopter rotors (vertically powered) shall have rings around
the perimeters
Projectile toys with stored energy (i.e.
controlled by the toy)
- Kinetic energy shall be < 0.08 J (for toys without resilient
impact surface)
- Kinetic energy shall be < 0.5 J (for toys with resilient
impact surfaces, e.g. rubber)
- Relevant warning is required in either one of the following 2 cases:
i)
The toy can discharge an object
other than that provided with the toy (the warning shall draw attention to the
hazards of using missiles other than those supplied or recommended by the
manufacturer)
ii)
If the kinetic energy is >
0.08 J, the following warning is needed:
“Warning! Do not aim at eyes or faces.”
20. AQUATIC TOYS
![]()
- Stopper shall be permanently attached
- Stopper shall stands < 5 mm from the surface of toy when
being pushed into the toy
- If the stopper is a small part, it shall not become detached
after torque/tension tests, even the toy is intended for children over 3 years
-
The following warning shall be
put:
“Warning! Only to be used in water in which the child
is within its depth and under supervision.”
Remark: The warning needs
to be put on BOTH the toy and pa
21. ACOUSTICS
![]()

-
The requirements apply to toys
which are manifestly designed to emit sound only
- The following Table shows the acoustic requirements in EN 71-1:2005 + A1:2007
|
|
Measurement
distance |
Parameter used
|
Frequency
Weighting
|
Limit
|
|
Close-to-the-ear toys without earphones |
2.5 cm |
Time average sound pressure level
|
A |
80 dB (A) |
Peak emission sound pressure level
|
C |
115 dB (C) |
||
|
Close-to-the-ear toys with earphones |
In ear coupler |
Time average sound pressure level
|
A |
90 dB (A) |
Peak emission sound pressure level
|
C |
115 dB (C) |
||
|
Rattles and Squeeze toys |
50 cm |
Sound exposure level
|
A |
85 dB (A) |
Peak emission sound pressure level
|
C |
110 dB (C) |
||
|
Toys using percussion caps |
50 cm |
Peak emission sound pressure level
|
C |
125 dB (C) |
|
Other sound producing toys
(hand-held toys and table-top/floor toys) |
50 cm |
Peak emission sound pressure level
|
C |
115 dB (C) |
sound
-
If the Peak emission sound
pressure levels are > 110 dB(C), the following warning is needed:
“Warning!
Do not use close to the ear! Misuse may cause damage to hearing.”
“Do not fire indoors” (for toys using percussion caps)
Please see below for reference:
Approx. sound
pressure levels
A quiet office 65
– 75 dB(C)
An office with speaking noises 85
– 105 dB(C)
A road with noisy traffics 100
– 120 dB(C)
A
construction site with piling machines 135 – 145 dB(C)
© 2008 Professional Testing & Consulting Ltd. All rights reserved.
 copy.gif)
 copy.gif)